NOTE!
Click on MENU to Browse between Subjects...17CS553 - ADVANCED JAVA AND J2EE
Answer Script for Module 5
Solved Previous Year Question Paper
CBCS SCHEME
ADVANCED JAVA AND J2EE
[As per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) scheme]
(Effective from the academic year 2019 -2020)
SEMESTER - V
Subject Code 17CS553
IA Marks 40
Number of Lecture Hours/Week 03
Exam Marks 60
These Questions are being framed for helping the students in the "FINAL Exams" Only
(Remember for Internals the Question Paper is set by your respective teachers).
Questions may be repeated, just to show students how VTU can frame Questions.
- ADMIN
Answer: JDBC driver specification classifies JDBC drivers into four groups.
Each group is referred to as a JDBC driver type and address a Specific need
for communicating with various DBMSs.
Type 1 JDBC-to-ODBC Driver.
The JDBC-to-ODBC Bridge, is used to translate DBMS calls between the JDBC
specification and the ODBC specification. The JDBC-to-ODBC driver receives
messages from a J2EE component that conforms to the JDBC specification.
Those messages are translated by the JDBC-to-ODBC driver into the ODBC
message format, which is then translated into the message format understood
by the DBMS. However, avoid using the JDBC/ODBC Bridge in a mission-critical
application because the extra translation might negatively impact
performance.
The
Java/Native Code driver
uses Java classes to generate platform-specific code—this, code only
understood by a specific DBMS. The manufacturer of the DBMS Provides both
the Java/ Native Code driver and API classes so the J2EE component can
generate, the platform-specific code. The obvious disadvantage of using a
Java/Native Code ° driver is the loss of some portability of code. The API
classes for the Java/Native Code driver probably won't work with another
manufacturer’s DBMS.
The
Type 3 JDBC driver
, also referred to as the Java Protocol, is the most common] used JDBC
driver. The Type 3 JDBC driver converts SQL queries into JOBC-formatted
statements. The JDBC-formatted statements are translated into the format
required by the DBMS.
The
Type 4 JDBC driver
is also known asthe Type 4 database protocol. This driver is similar to the
Type 3 JDBC driver except SQL queries are translated into the format
required by the DBMS. SQL queries do not need to be converted to
JDBC-formatted systems. This is the fastest way to communicate SQL queries
to the DBMS.
Answer:
The Statement object
is used whenever a J2EE component needs to immediately execute a query
without first having the query compiled. The Statement object contains the
executeQuery() method, which is passed the query as an argument. The query
is then transmitted to the DBMS for processing.
The executeQuery() method returns one ResultSet object that contains rows,
columns, and metadata that represent data requested by query. The ResultSet
object also contains methods that are used to manipulate data in the
ResultSet.
The execute() method of the Statement object is used when there may be
multiple results returned. A third commonly used method of the Statement
object is the executeUpdate() method. The executeUpdate() method is used to
execute queries that contain UPDATE and DELETE SQL statements, which changes
values in a row and removes a row respectively. The executeUpdate() method
returns an integer indicating the numberof rows that were updated by the
query. The executeUpdate() is used to INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and DDL
statements.
PreparedStatement Object
ASQL query must be compiled before the DBMS processes the query. Compiling
occurs after one of the Statement object’s execution methods is called.
Compiling a query is an overhead that is acceptable if the query is called
once. However, the compiling process can become an expensive overhead if the
query is executed several times by the same instance of the J2EE component
during the same session.
A SQL query can be precompiled and executed by using the PreparedStatement
object. In this case, the query is constructed similar to queries that were
illustrated previously in the chapter. However, a question mark is used as a
placeholder for a value that is inserted into the query after the query is
compiled. It is this value that changes each time the query is executed.
The advantage of using the PreparedStatement object is that the query is
precompiled once and the setxxx() method called as needed to change the
specified values of the query Without having to recompile the query. The
PreparedStatement objectalso has an execute() method and an executeUpdate()
method, as described in the previous section.
The precompiling is performed by the DBMSandis referred to as “late
binding.’ When the DBMS receives the request, the DBMS attempts to match the
query to a previously compiled query. If found, then parameters passed to
the query using the setxxx() methods are bound and the query is executed. If
not found, then the query is compiled and retained by the DBMS for later
use.
The
CallableStatement
object is used to call a stored procedure from within J2EE object. A stored
procedure is block of code and is identified by unique name. the code can be
written in Transact-C, PL/SQL.
Stored procedure is executed by invoking by the name of procedure.
The callableStatement uses three types of parameter when calling stored
procedure. The parameters are IN, OUT, INOUT.
IN parameter contains data that needs to be passed to the stored procedure
whose value is assigned using setxxx() method.
OUT parameter contains value returned by stored procedure. The OUT
parameter should be registers by using registerOutParameter() method and
then later retrieved by the J2EE component using getxxx() method.
INOUT parameter is used to both pass information to the stored procedure
and retrieve the information from the procedure.
Using CallableStatement objects is much like using PreparedStatement
objects. You must bind values to all parameters before executing the
statement, or you will receive an SQLException. If you have IN parameters,
just follow the same rules and techniques that apply to a PreparedStatement
object; use the setXXX() method that corresponds to the Java data type you
are binding.
When you use OUT and INOUT parameters you must employ an additional
CallableStatement method, registerOutParameter(). The registerOutParameter()
method binds the JDBC data type to the data type the stored procedure is
expected to return. Once you call your stored procedure, you retrieve the
value from the OUT parameter with the appropriate getXXX() method. This
method casts the retrieved value of SQL type to a Java data type.
1. Loading the JDBC driver
• The jdbc driver must be loaded before the J2EE component can be connected
to the database.
• Driver is loaded by calling the method and passing it the name of driver
Class.forName(“sun:jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver”);
2. Connecting to the DBMS.
• Once the driver is loaded, J2EE component must connect to the DBMS using
DriverManager.getConnection() method.
• It is highest class in hierarchy and is responsible for managing driver
information.
• It takes three arguments URL, User, Password
• It returns connection interface that is used throughout the process to
reference a database
String url=”jdbc:odbc:JdbcOdbcDriver”;
String userId=”jim”
String password=”Keogh”;
Statement DatRequest;
Private Connection db;
try{
Class.forName(“sun:jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver”);
Db=DriverManager.getConnection(url,userId,password);
}
3. Creating and Executing a statement.
• The next step after the JDBC is loaded and connection is successfully
made with a particular database managed by the dbms, is to end a particular
query to the DBMS for processing.
• SQL query consists series of SQL command that direct DBMS to do something
example Return rows.
• Connect.createStatement() method is used to create a statement Object.
• The statement object is then used to execute a query and return result
object that contain response from the DBMS
Statement DataRequest;
ResultSet Results;
try {
String query=“select * from Customers”;
DataRequest=Database.createStatement();
Results= DataRequests.executeQuery(query);
}
4. Processing data returned by the DBMS
•
java.sql.ResultSet
object is assigned the result received from the DBMS after the query is
processed.
•
java.sql.ResultSet
contain method to interact with data that is returned by the DBMS to the
J2EE Component.
Results= DataRequests.executeQuery(query);
do
{
Fname=Results.getString(Fname)
}
While(Results.next())
In the above code it return result from the query and executes the query.
And getString is used to process the String retrieved from the database.
Terminating the connection with the DBMS.
To terminate the connection Database.close() method is used.
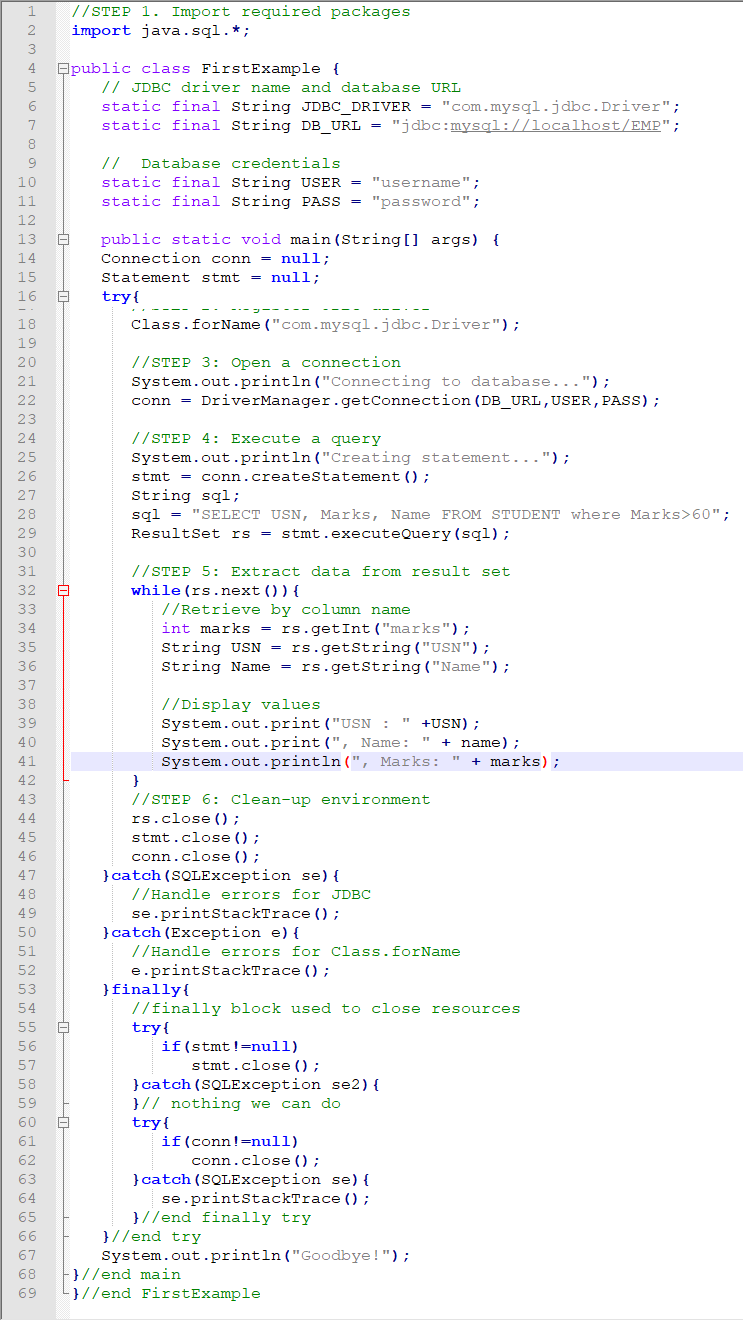
Refer 1st Question & Answer.
Below Page NAVIGATION Links are Provided...
All the Questions on Question Bank Is SOLVED
Follow our Instagram Page:
FutureVisionBIE
https://www.instagram.com/futurevisionbie/
Message: I'm Unable to Reply to all your Emails
so, You can DM me on the Instagram Page & any other Queries.

 MENU
MENU

