NOTE!
Click on MENU to Browse between Subjects...17CS53 - DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Answer Script for Module 1
Solved Previous Year Question Paper
CBCS SCHEME
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
17CS53
[As per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) scheme]
(Effective from the academic year 2019 -2020)
SEMESTER - V
Subject Code 17CS53
IA Marks 40
Number of Lecture Hours/Week 04
Exam Marks 60
These Questions are being framed for helping the students in the "FINAL Exams" Only
(Remember for Internals the Question Paper is set by your respective teachers).
Questions may be repeated, just to show students how VTU can frame Questions.
- ADMIN
User-friendly interfaces provided by a DBMS may include the following:
1.1 Menu-based Interfaces for Web Clients or Browsing
.
These interfaces present the user with lists of options (called menus) that
lead the user through the formulation of a request. Menus do away with the
need to memorize the specific commands and syntax of a query language;
rather, the query is composed step-bystep by picking options from a menu
that is displayed by the system. Pull-down menus are a very popular
technique in Web-based user interfaces. They are also often used in
browsing interfaces, which allow a user to look through the contents of a
database in an exploratory and unstructured manner.
1.2 Apps for Mobile Devices.
These interfaces present
mobile users with access to their data. For example, banking, reservations,
and insurance companies, among many others, provide apps that allow users
to access their data through a mobile phone or mobile device. The apps have
built-in programmed interfaces that typically allow users to login using
their account name and password; the apps then provide a limited menu of
options for mobile access to the user data, as well as options such as
paying bills (for banks) or making reservations (for reservation Web
sites).
1.3 Forms-based Interfaces.
A forms-based interface
displays a form to each user. Users can fill out all of the form entries to
insert new data, or they can fill out only certain entries, in which case
the DBMS will retrieve matching data for the remaining entries. Forms are
usually designed and programmed for naive users as interfaces to canned
transactions.
1.4 Graphical User Interfaces.
A GUI typically displays a
schema to the user in diagrammatic form. The user then can specify a query
by manipulating the diagram. In many cases, GUIs utilize both menus and
forms.
1.5 Natural Language Interfaces.
These interfaces accept
requests written in English or some other language and attempt to
understand them. A natural language interface usually has its own schema,
which is similar to the database conceptual schema, as well as a dictionary
of important words. The natural language interface refers to the words in
its schema, as well as to the set of standard words in its dictionary, that
are used to interpret the request.
1.6 Keyword-based Database Search.
These are somewhat
similar to Web search engines, which accept strings of natural language
(like English or Spanish) words and match them with documents at specific
sites (for local search engines) or Web pages on the Web at large (for
engines like Google or Ask). They use predefined indexes on words and use
ranking functions to retrieve and present resulting documents in a
decreasing degree of match.
1.7 Speech Input and Output
. Limited use of speech as an
input query and speech as an answer to a question or result of a request is
becoming commonplace. Applications with limited vocabularies, such as
inquiries for telephone directory, flight arrival/departure, and credit
card account information, are allowing speech for input and output to
enable customers to access this information. The speech input is detected
using a library of predefined words and used to set up the parameters that
are supplied to the queries. For output, a similar conversion from text or
numbers into speech takes place.
1.8 Interfaces for Parametric Users.
Parametric users,
such as bank tellers, often have a small set of operations that they must
perform repeatedly. For example, a teller is able to use single function
keys to invoke routine and repetitive transactions such as account deposits
or withdrawals, or balance inquiries. Systems analysts and programmers
design and implement a special interface for each known class of naive
users. Usually a small set of abbreviated commands is included, with the
goal of minimizing the number of keystrokes required for each request.
1.9 Interfaces for the DBA.
Most database systems contain
privileged commands that can be used only by the DBA staff. These include
commands for creating accounts, setting system parameters, granting account
authorization, changing a schema, and reorganizing the storage structures
of a database.
Figure 13.1 shows a simplified overview of the database design process. The
first step shown is requirements collection and analysis
.
During this step, the database designers interview prospective database
users to understand and document their data requirements
.
The result of this step is a concisely written set of users' requirements. These requirements should be specified in as detailed and complete a form as possible.
In parallel with specifying the data requirements, it is useful to specify
the known functional requirements
of the application.
These consist of the user defined operations
(or transactions
) that will be applied to the database,
including both retrievals and updates. In software design, it is common to
use
data flow diagrams, sequence diagrams, scenarios, and other techniques
to specify functional requirements.
Once the requirements have been collected and analyzed, the next step is to create a conceptual schema for the database, using a high-level conceptual data model.
This step is called conceptual design. The conceptual schema is a concise description of the data requirements of the users and includes detailed descriptions of the entity types, relationships, and constraints; these are expressed using the concepts provided by the high-level data model.
The high-level conceptual schema can also be used as a reference to ensure that all users' data requirements are met and that the requirements do not conflict. This approach enables database designers to concentrate on specifying the properties of the data, without being concerned with storage and implementation details, which makes it is easier to create a good conceptual database design.
The next step in database design is the actual implementation of the
database, using a commercial DBMS. Most current commercial DBMSs use an
implementation data model-such as the relational (SQL) model-so the
conceptual schema is transformed from the high-level data model into the
implementation data model. This step is called logical design or data model
mapping; its result is a
database schema in the implementation data model of the DBMS. Data model
mapping is often automated or semi-automated within the database design
tools.
The last step is the physical design phase
, during which
the internal storage structures, file organizations, indexes, access paths,
and physical design parameters for the database files are specified. In
parallel with these activities, application programs are designed and
implemented as database transactions corresponding to the high-level
transaction specifications.
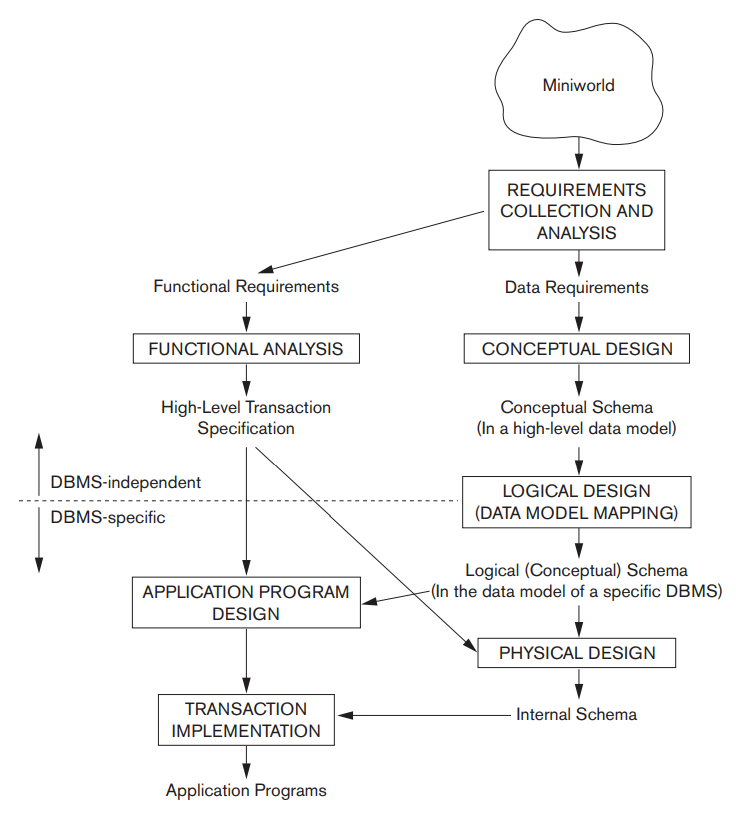
Fig 13.1: A simplified diagram to illustrate the main phases of database design.
Below Page NAVIGATION Links are Provided...
All the Questions on Question Bank Is SOLVED
Follow our Instagram Page:
FutureVisionBIE
https://www.instagram.com/futurevisionbie/
Message: I'm Unable to Reply to all your Emails
so, You can DM me on the Instagram Page & any other Queries.

 MENU
MENU

