NOTE!
Click on MENU to Browse between Subjects...17CS664 - PYTHON APPLICATION PROGRAMMING
Answer Script for Module 1
Solved Previous Year Question Paper
CBCS SCHEME
PYTHON APPLICATION PROGRAMMING
[As per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) scheme]
(Effective from the academic year 2017 - 2018)
SEMESTER - VI
Subject Code 17CS664
IA Marks 40
Number of Lecture Hours/Week 3
Exam Marks 60
These Questions are being framed for helping the students in the "FINAL Exams" Only
(Remember for Internals the Question Paper is set by your respective teachers).
Questions may be repeated, just to show students how VTU can frame Questions.
- ADMIN
ANSWER :
1.1 ITERATION
Iteration is a processing repeating some task. In a real time programming, we require a set of statements to be repeated certain number of times and/or till a condition is met. Every programming language provides certain constructs to achieve the repetition of tasks. Most used Iterator are While & for.
1.1.1 The while Statement
The while loop has the syntax as below -

Here, while
is a keyword. The condition is
evaluated first. Till its value remains true, the statement_1 to
statement_n will be executed. When the condition becomes false, the loop is
terminated and statements after the loop will be executed. Consider an
example -
1.1.2 While Structure:
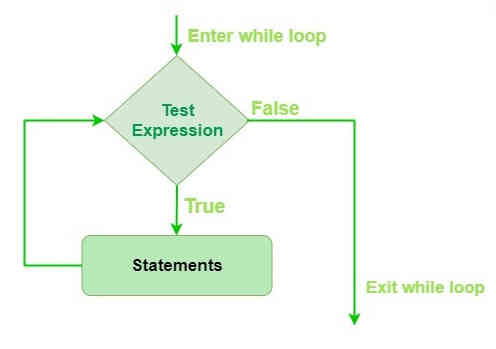
When a while loop is executed, expr is first evaluated in a Boolean context and if it is true, the loop body is executed.
Then the expr is checked again, if it is still true then the
body is executed again and this continues until the expression becomes
false.
1.1.3 Example - 1:
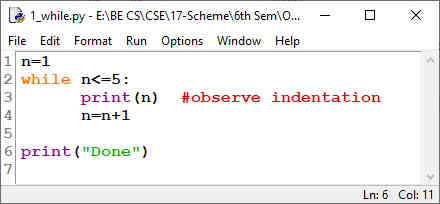
Fig 1.3 Program of while
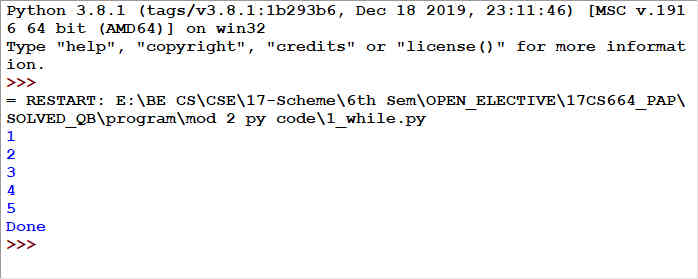
Fig 1.4: Output of Fig 1.3
In the above example, a variable n is initialized to 1. Then the condition
n<=5 is being checked. As the condition is true, the block of code
containing print statement (print(n)) and increment statement (n=n+1) are
executed. After these two lines, condition is checked again. The procedure
continues till condition becomes false, that is when n becomes 6. Now, the
while-loop is terminated and next statement after the loop will be
executed. Thus, in this example, the loop is iterated
for 5 times.
Note that, a variable n is initialized before starting the loop and it is
incremented inside the loop. Such a variable that changes its value for
every iteration and controls the total execution of the loop is called asiteration variable
or counter variable
. If the count variable is not
updated properly within the loop, then the loop may not terminate and keeps
executing infinitely.
1.1.4 Single statement while block
Just like the if block, if the while block
consists of a single statement the we can declare the entire loop in a
single line. If there are multiple statements in the block that makes up
the loop body, they can be separated by semicolons (;).

Fig 1.5 Program to demonstrate Single Statement while Block
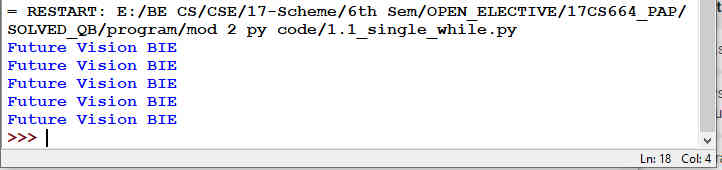
Fig 1.6: Output of Fig 1.5
1.1.5 The break Statement
With the
break
statement we can stop the
loop even if the while condition is true:
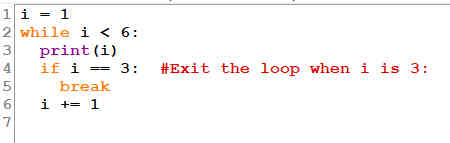
Fig 1.7: Break in while Statement
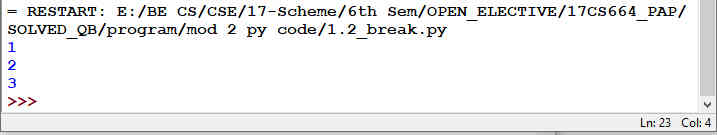
Fig 1.8: Output for Fig 1.7
1.1.6 The continue Statement:
With the continue statement we can stop the current iteration, and continue with the next:
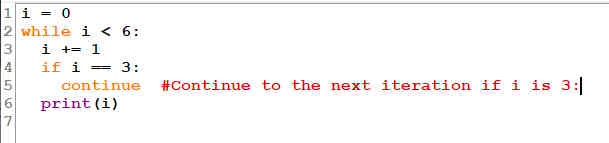
Fig 1.9: Continue in While Loop
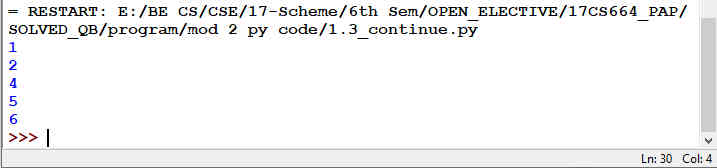
Fig 1.10: Output of Fig 1.9
1.1.7 The else Statement
With the else statement we can run a block of code once when the condition no longer is true:
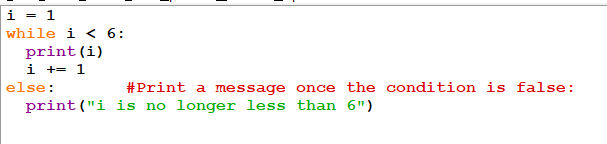
Fig 1.11: Use of Else in while statement
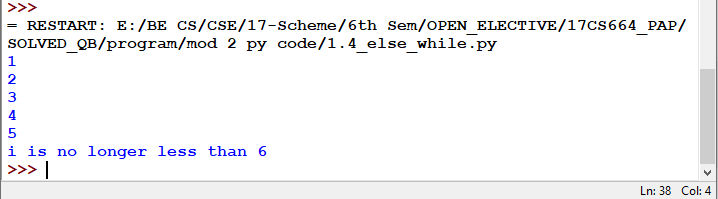
Fig 1.12: Output of Fig 1.11
ANSWER :
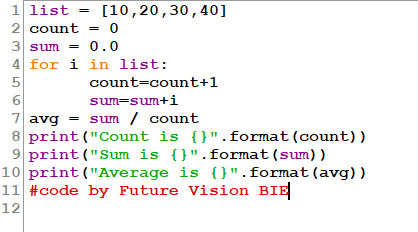
Fig 2.1: Program to demonstrate Counting Summing & Average using Looping Statement - for loop

Fig 2.2: Output of Fig 2.1
ANSWER :
3.1 String:
A string is a sequence of characters. You can access the characters one at a time with the bracket operator:
>>>
fruit = 'banana'
>>>
letter = fruit[1]
The second statement extracts the character at index position 1 from the fruit variable and assigns it to the letter variable. The expression in brackets is called an index. The index indicates which character in the sequence you want (hence the name).
3.2 Traversal of String using with a loop:
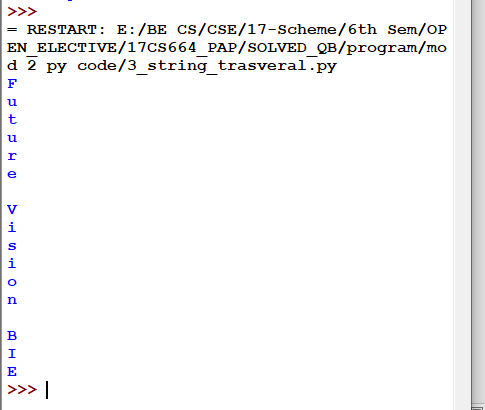
3.2.1 Using For Loop:
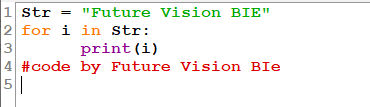
Fig 3.1: Traversal using for loop
3.2.2 Using while loop:

Fig 3.3: Traversal using While Statement
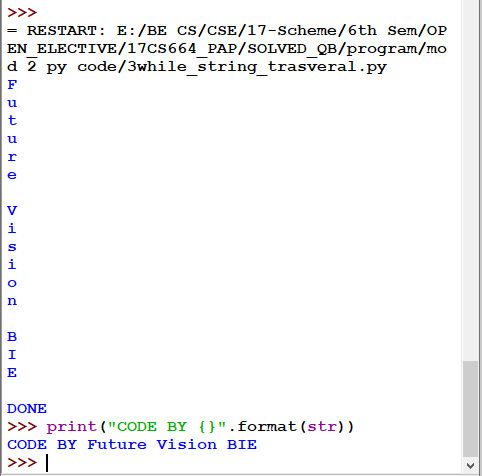
Fig 3.4: Output of Fig 3.3
ANSWER :
4.1 While loop:
Refer 1st
Question & Answer or Click Here
4.2 for loop:
The while loop iterates till the condition is met and hence, the
number of iterations are usually unknown prior to the loop. Hence, it is
sometimes called as indefinite loop. When we know total number of
times the set of statements to be executed, for
loop will be used. This is called as a definite loop.
The for-loop iterates over a set
of numbers, a set of words, lines in a file etc. The syntax of for-loop
would be -

Here,
for
and in
are keywords
List/sequence
is a set of elements on which the loop is iterated. That is, the loop will
be executed till there is an element in list/sequence
Statements
constitutes body of the loop
4.2.1 Example:
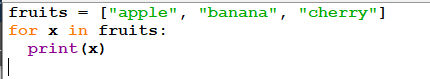
Fig 4.2 Demonstrating for looping Statement

Fig 4.3: Output for Fig 4.2
4.2.2 Looping through a String:
Refer 3rd Question & Answer.
4.2.3 The break Statement: (same as in While Loop)
With the break statement we can stop the loop before it has looped through all the items:

Fig 4.4: Break Statement in For Loop
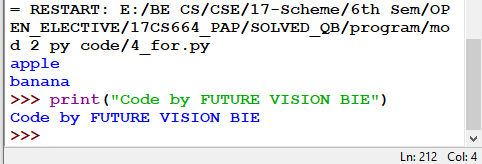
Fig 4.5: Output of Fig 4.4
4.2.4 The continue Statement: (same as in While Loop)
With the continue statement we can stop the current iteration of the loop, and continue with the next:

Fig 4.6: Continue Statement in for loop
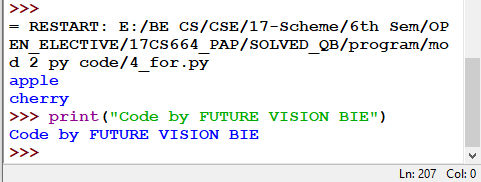
Fig 4.7: Output for Fig 4.6
4.2.5 The range( ) Function:
To loop through a set of code a specified number of times, we can use the range( ) function,
The range( ) function returns a sequence of numbers, starting from 0 by default, and increments by 1 (by default), and ends at a specified number.
range(init value, ending number, increment value)

Fig 4.8: range function Demonstartion
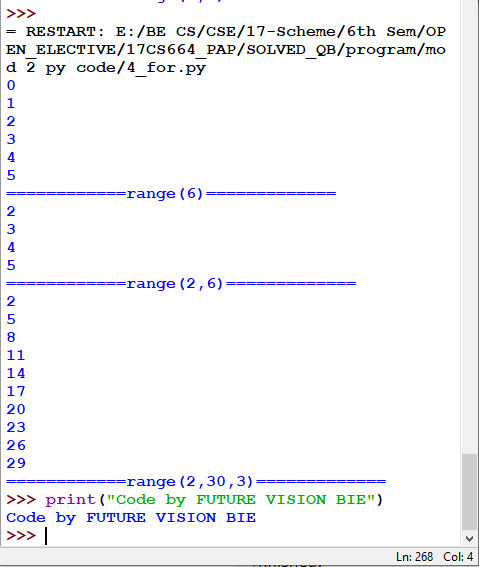
Fig 4.9: Output of Fig 4.8
4.2.6 Nested Loops:
A nested loop is a loop inside a loop.
The "inner loop" will be executed one time for each iteration of the "outer loop":
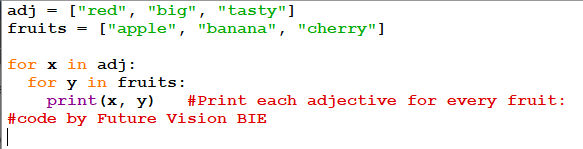
Fig 4.10: Nested For loop statement
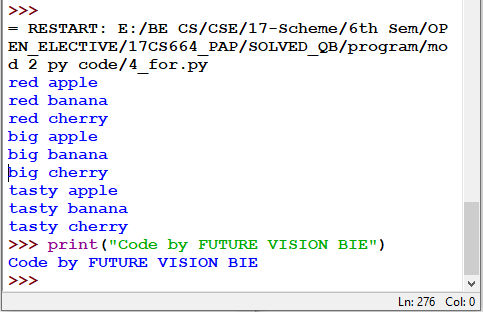
Fig 4.11: Output for Fig 4.10
4.2.7 The pass Statement
for
loops cannot be empty, but if you for some reason have a for
loop with no content, put in the pass statement to avoid
getting an error.
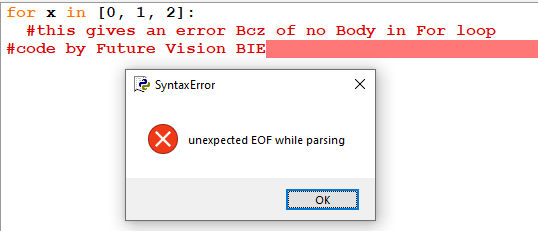
Fig 4.12: Error Because There is no Body in for loop

Fig 4.13: Use of pass keyword in for loop for empty body

Fig 4.14: Output for Fig 4.13
ANSWER :
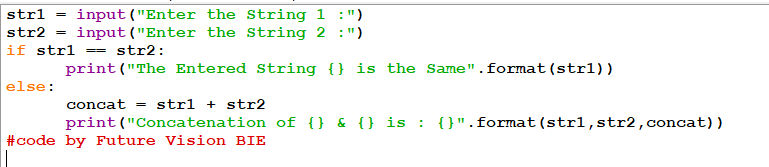
Fig 5.1 Program to compare String & concatenate if both strings are not same.
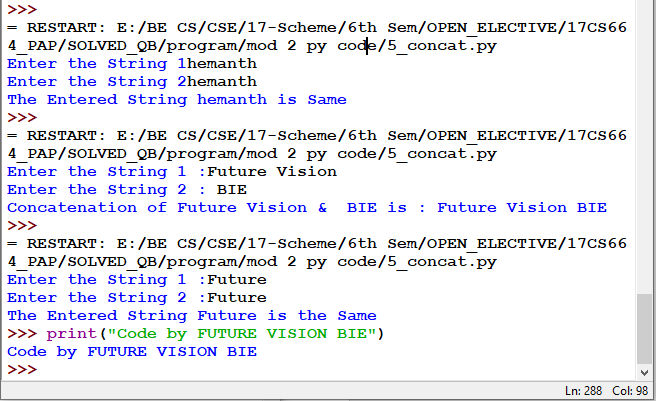
Fig 5.2: Output for Fig 5.1
Below Page NAVIGATION Links are Provided...
All the Questions on Question Bank Is SOLVED

 MENU
MENU

