NOTE!
Click on MENU to Browse between Subjects...17CS664 - PYTHON APPLICATION PROGRAMMING
Answer Script for Module 1
Solved Previous Year Question Paper
CBCS SCHEME
PYTHON APPLICATION PROGRAMMING
[As per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) scheme]
(Effective from the academic year 2017 - 2018)
SEMESTER - VI
Subject Code 17CS664
IA Marks 40
Number of Lecture Hours/Week 3
Exam Marks 60
These Questions are being framed for helping the students in the "FINAL Exams" Only
(Remember for Internals the Question Paper is set by your respective teachers).
Questions may be repeated, just to show students how VTU can frame Questions.
- ADMIN
ANSWER :
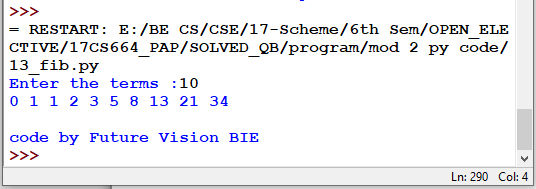
11.1 Using Recursive:

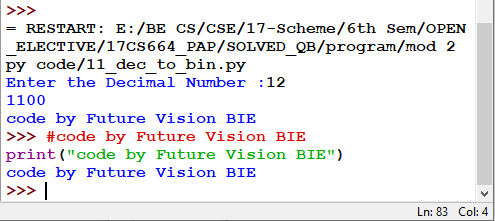
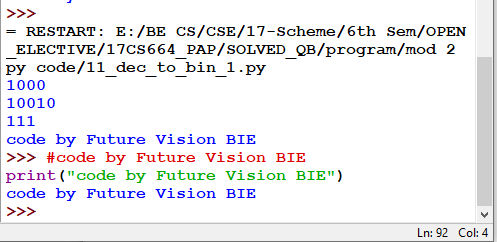
11.2 Method 2 using Build-in Function

ANSWER :
12.1 Table with all methods of Strings:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
casefold() |
Converts string into lower case |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
encode() |
Returns an encoded version of the string |
|
endswith() |
Returns true if the string ends with the specified value |
|
expandtabs() |
Sets the tab size of the string |
|
|
|
|
format() |
Formats specified values in a string |
|
format_map() |
Formats specified values in a string |
|
index() |
Searches the string for a specified value and returns the position of where it was found |
|
isalnum() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are alphanumeric |
|
isalpha() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are in the alphabet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
isidentifier() |
Returns True if the string is an identifier |
|
islower() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are lower case |
|
isnumeric() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are numeric |
|
isprintable() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are printable |
|
isspace() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are whitespaces |
|
istitle() |
Returns True if the string follows the rules of a title |
|
isupper() |
Returns True if all characters in the string are upper case |
|
join() |
Joins the elements of an iterable to the end of the string |
|
ljust() |
Returns a left justified version of the string |
|
|
|
|
lstrip() |
Returns a left trim version of the string |
|
maketrans() |
Returns a translation table to be used in translations |
|
partition() |
Returns a tuple where the string is parted into three parts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rindex() |
Searches the string for a specified value and returns the last position of where it was found |
|
rjust() |
Returns a right justified version of the string |
|
rpartition() |
Returns a tuple where the string is parted into three parts |
|
rsplit() |
Splits the string at the specified separator, and returns a list |
|
rstrip() |
Returns a right trim version of the string |
|
|
|
|
splitlines() |
Splits the string at line breaks and returns a list |
|
startswith() |
Returns true if the string starts with the specified value |
|
|
|
|
swapcase() |
Swaps cases, lower case becomes upper case and vice versa |
|
title() |
Converts the first character of each word to upper case |
|
translate() |
Returns a translated string |
|
|
|
|
zfill() |
Fills the string with a specified number of 0 values at the beginning |
12.2 Six Methods with Examples:
12.2.1 Capitalize:
Definition and Usage:
The capitalize() method returns a string where the first character is upper case.
Syntax:
string.capitalize()
Parameter Values:
No parameters
12.2.2 String center() Method
Definition and Usage
The center() method will center align the string, using a specified character (space is default) as the fill character.
Syntax
string.center(length, character)
Parameter Values:
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
length |
Required. The length of the returned string |
|
character |
Optional. The character to fill the missing space on each side. Default is " " (space) |
12.2.3 String count() Method
Definition and Usage
The count() method returns the number of times a specified value appears in the string.
Syntax
string.count(value, start, end)
Parameter Values
|
|
|
|
value |
Required. A String. The string to value to search for |
|
start |
Optional. An Integer. The position to start the search. Default is 0 |
|
end |
Optional. An Integer. The position to end the search. Default is the end of the string |
12.2.4 String find() Method
Definition and Usage
The find() method finds the first occurrence of the specified value.
The find() method returns -1 if the value is not found.
The find() method is almost the same as the index() method, the only difference is that the index() method raises an exception if the value is not found. (See example below)
Syntax
string.find(value, start, end)
Parameter Values
|
|
|
|
value |
Required. The value to search for |
|
start |
Optional. Where to start the search. Default is 0 |
|
end |
Optional. Where to end the search. Default is to the end of the string |
12.2.5 String isdigit() Method
Definition and Usage
The isdigit() method returns True if all the characters are digits, otherwise False.
Exponents, like ², are also considered to be a digit.
Syntax
string.isdigit()
Parameter Values
No parameters.
12.2.6 String lower() Method
Definition and Usage
The lower() method returns a string where all characters are lower case.
Symbols and Numbers are ignored.
Syntax
string.lower()
Parameter Values
No parameters
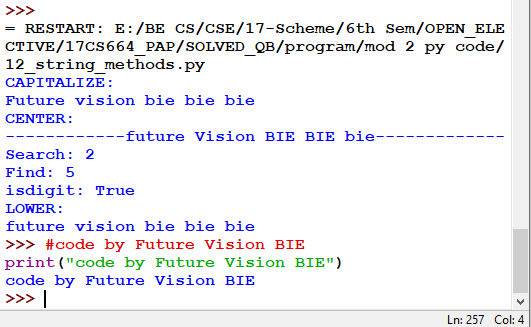
12.3 Program Demonstrating all the six methods:

ANSWER :
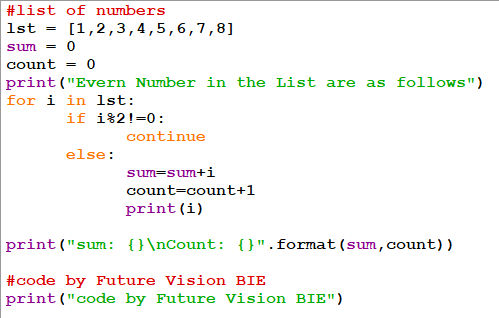
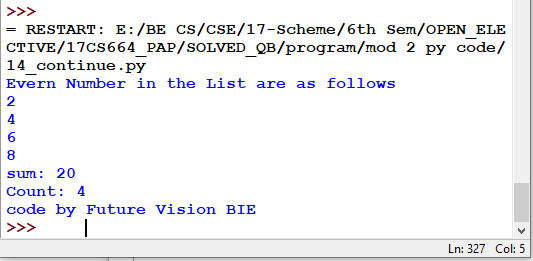
14.1 Continue:
Continue is also a loop control statement just like the break statement. continue statement is opposite to that of break statement, instead of terminating the loop, it forces to execute the next iteration of the loop.
As the name suggests the continue statement forces the loop to continue or execute the next iteration. When the continue statement is executed in the loop, the code inside the loop following the continue statement will be skipped and the next iteration of the loop will begin.
14.2 Program:
ANSWER :
15.1 Refer 3rd
Question & Answer or Click Here
15.2 Refer 12th
Question & Answer or Click Here
Below Page NAVIGATION Links are Provided...
All the Questions on Question Bank Is SOLVED

 MENU
MENU