×
NOTE!
Click on MENU to Browse between Subjects...
Advertisement
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS LABORATORY
(Effective from the academic year 2018 -2019)
SEMESTER - IV
Course Code 18CSL47
CIE Marks 40
Number of Contact Hours/Week 0:2:2
SEE Marks 60
Total Number of Lab Contact Hours 36
Exam Hours 03
Experiments 12
Design and implement in Java to find all Hamiltonian Cycles in a connected undirected Graph G of n vertices using backtracking principle.
Advertisement
Advertisement
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 | import java.util.Scanner; class Hamiltonian { static int[][] graph; static int[] soln; static int n, count = 0; public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter Number of Vertices"); n = scan.nextInt(); // Read Adjacency Matrix in Graph array(1 Indexed) graph = new int[n + 1][n + 1]; System.out.println("Enter Adjacency Matrix"); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { graph[i][j] = scan.nextInt(); } } scan.close(); // Instatiate Solution array(1 Indexed), (Default Value is 0) soln = new int[n + 1]; System.out.println("Hamiltonian Cycle are"); // In a cycle source vertex doesn't matter // Assign Starting Point to prevent repetitions soln[1] = 1; // Call Hamiltonian function to start backtracking from vertex 2 hamiltonian(2); if (count == 0) { System.out.println("No Hamiltonian Cycle"); } } static void hamiltonian(int k) { while (true) { nextValue(k); // No next vertex so return if (soln[k] == 0) { return; } // if cycle is complete then print it else find next vertex if (k == n) { printArray(); } else { hamiltonian(k + 1); } } } static void nextValue(int k) { // Finds next feasible value while (true) { soln[k] = (soln[k] + 1) % (n + 1); // If no next vertex is left, then return if (soln[k] == 0) { return; } // If there exists an edge if (graph[soln[k - 1]][soln[k]] != 0) { int j; // Check if the vertex is not repeated for (j = 1; j < k; j++) { if (soln[j] == soln[k]) { break; } } // If vertex is not repeated if (j == k) { // If the vertex is not the last vertex or it completes the cycle then return if (k < n || (k == n && graph[soln[n]][soln[1]] != 0)) { return; } } } } } static void printArray() { count += 1; // Print Solution Array for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { System.out.print(soln[i] + " "); } System.out.println(soln[1]); } } |
Advertisement
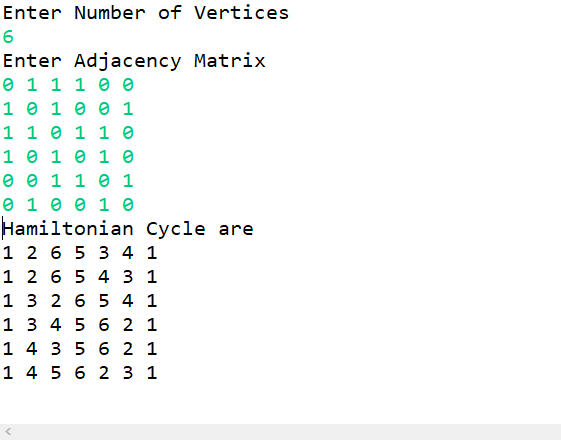
Fig 12.1: Output .
×
Note
Please Share the website link with Your Friends and known Students...
-ADMIN
-ADMIN
×
Note
Page Number is specified to navigate between Pages...
T = Text book
QB = Question Bank
AS = Amswer Script
-ADMIN
T = Text book
QB = Question Bank
AS = Amswer Script
-ADMIN
Advertisement

 MENU
MENU

